#Apache Solr Query Language
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text

#Solr Query Syntax#Apache Solr Query Language#Solr Search Query Examples#Solr Query Parameters#Solr Query Filters#Solr Advanced Query Syntax#solr query#solr in query#Master Solr Query Syntax
0 notes
Text
What is Solr – Comparing Apache Solr vs. Elasticsearch

In the world of search engines and data retrieval systems, Apache Solr and Elasticsearch are two prominent contenders, each with its strengths and unique capabilities. These open-source, distributed search platforms play a crucial role in empowering organizations to harness the power of big data and deliver relevant search results efficiently. In this blog, we will delve into the fundamentals of Solr and Elasticsearch, highlighting their key features and comparing their functionalities. Whether you're a developer, data analyst, or IT professional, understanding the differences between Solr and Elasticsearch will help you make informed decisions to meet your specific search and data management needs.
Overview of Apache Solr
Apache Solr is a search platform built on top of the Apache Lucene library, known for its robust indexing and full-text search capabilities. It is written in Java and designed to handle large-scale search and data retrieval tasks. Solr follows a RESTful API approach, making it easy to integrate with different programming languages and frameworks. It offers a rich set of features, including faceted search, hit highlighting, spell checking, and geospatial search, making it a versatile solution for various use cases.
Overview of Elasticsearch
Elasticsearch, also based on Apache Lucene, is a distributed search engine that stands out for its real-time data indexing and analytics capabilities. It is known for its scalability and speed, making it an ideal choice for applications that require near-instantaneous search results. Elasticsearch provides a simple RESTful API, enabling developers to perform complex searches effortlessly. Moreover, it offers support for data visualization through its integration with Kibana, making it a popular choice for log analysis, application monitoring, and other data-driven use cases.
Comparing Solr and Elasticsearch
Data Handling and Indexing
Both Solr and Elasticsearch are proficient at handling large volumes of data and offer excellent indexing capabilities. Solr uses XML and JSON formats for data indexing, while Elasticsearch relies on JSON, which is generally considered more human-readable and easier to work with. Elasticsearch's dynamic mapping feature allows it to automatically infer data types during indexing, streamlining the process further.
Querying and Searching
Both platforms support complex search queries, but Elasticsearch is often regarded as more developer-friendly due to its clean and straightforward API. Elasticsearch's support for nested queries and aggregations simplifies the process of retrieving and analyzing data. On the other hand, Solr provides a range of query parsers, allowing developers to choose between traditional and advanced syntax options based on their preference and familiarity.
Scalability and Performance
Elasticsearch is designed with scalability in mind from the ground up, making it relatively easier to scale horizontally by adding more nodes to the cluster. It excels in real-time search and analytics scenarios, making it a top choice for applications with dynamic data streams. Solr, while also scalable, may require more effort for horizontal scaling compared to Elasticsearch.
Community and Ecosystem
Both Solr and Elasticsearch boast active and vibrant open-source communities. Solr has been around longer and, therefore, has a more extensive user base and established ecosystem. Elasticsearch, however, has gained significant momentum over the years, supported by the Elastic Stack, which includes Kibana for data visualization and Beats for data shipping.
Document-Based vs. Schema-Free
Solr follows a document-based approach, where data is organized into fields and requires a predefined schema. While this provides better control over data, it may become restrictive when dealing with dynamic or constantly evolving data structures. Elasticsearch, being schema-free, allows for more flexible data handling, making it more suitable for projects with varying data structures.
Conclusion
In summary, Apache Solr and Elasticsearch are both powerful search platforms, each excelling in specific scenarios. Solr's robustness and established ecosystem make it a reliable choice for traditional search applications, while Elasticsearch's real-time capabilities and seamless integration with the Elastic Stack are perfect for modern data-driven projects. Choosing between the two depends on your specific requirements, data complexity, and preferred development style. Regardless of your decision, both Solr and Elasticsearch can supercharge your search and analytics endeavors, bringing efficiency and relevance to your data retrieval processes.
Whether you opt for Solr, Elasticsearch, or a combination of both, the future of search and data exploration remains bright, with technology continually evolving to meet the needs of next-generation applications.
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
Kisaran Gaji Full Stack Developer di Indonesia

Full Stack Developer menjadi salah satu profesi yang semakin banyak dicari oleh perusahaan di Indonesia. Selain memiliki peranan yang penting dalam pengembangan web perusahaan. Nah bagi Anda yang ingin menjadi Full Stack Developer perlu mengetahui kisaran gaji Full Stack Developer di Indonesia yang akan kami bahas di artikel kali ini.
Gaji Full Stack Developer
Dilansir dari neuvoo.com, kisaran gaji Full Stack Developer di Indonesia mulai dari Rp. 8,000,000 sampai dengan Rp. 13,600,000 perbulan. Gaji yang besar tentunya dibutuhkan tanggung jawab yang besar juga. Oleh karena itu, untuk menjadi Full Stack Developer, Anda harus menguasai teknologi yang diperlukan Full Stack Developer seperrti :
1. System Administration
Linux dan basic shell scripting
Cloud computing: Amazon, Rackspace, etc.
Background processing: Gearman, Redis
Search: Elasticsearch, Sphinx, Solr
Caching: Varnish, Memcached, APC / OpCache
Monitoring: Nagios
2. Web Development Tools
Version control: Git, Mercurial, SVN
Virtualisasi: VirtualBox, Vagrant, Docker
3. Back-End Tech
Web servers: Apache, Nginx
Programming language: PHP, NodeJS, Ruby
Database: MySQL, MongoDB, Cassandra, Redis, SQL / JSON secara umum
4. Front-End Tech
HTML / HTML5: Semantic web
CSS / CSS3: LESS, SASS, Media Queries
JavaScript: jQuery, AngularJS, Knockout, etc.
Compatibility quirks across browsers
Responsive design
AJAX, JSON, XML, WebSocket
5. Design
Converting website design into front-end code
UI
UX
6. Mobile technologies
iOS
Android
Hybrid: Phonegap, Appcelerator
Menjadi seorang Full Stack Developer tidaklah mudah, Anda harus mempunyai pikiran yang terbuka akan teknologi baru. Anda harus bisa menggunakan setiap teknologi yang telah disebutkan diatas, dan harus mengerti bagaimana sebuah aplikasi dibuat, mulai dari konsep hingga menjadi produk jadi.
Menjadi seorang Full Stack Developer bukan berarti harus ahli, terbiasa akan semua teknologi yang ada karena spesialisasi ada untuk alasan tersebut. “full-stack developer” lebih kepada pengertian akan setiap area dan teknologi yang telah disebutkan diatas, bisa berkomunikasi dengan baik dengan rekan kerja, dan bisa menjadi aset yang berguna jika memang situasi memerlukan akan pengetahuan tersebut.
Baca juga : Tugas Full Stack Developer yang Wajib Dilakukan
1 note
·
View note
Text
Vufind-Search. Discover. Share.

Vufind is an open source library resource portal designed and developed for libraries. It is a library search engine that allows users to search and browse beyond the resources of a traditional online public access catalogue. This software was developed by Villanova University.
Visit
Category:
Open Source
Description
The software works with a simplified interface and provides easy keyword searching, the most frequently used software for searching catalog records and looking for other library resources including locally cached publications, digital library products and institutional repository and bibliography. Vufind is also modular and extremely configurable, enabling implementer to choose system components to suit their needs.
VuFind offers a number of features that enhance usability:
Faceted search results that allow users to narrow items by format, call number, language, author, genre, era, region, and more
Suggested resources and searches
Browsing capability
Personal organization and annotation of resources through favorites lists, texting, e-mailing, tagging, and commenting features
Persistent URLs
APA or MLA citations
Author biographies
Multi-language capability with translations available in Brazilian Portuguese, Chinese, Czech, Dutch, English, French, German, Japanese, Spanish, Bengali (India) and more
VuFind runs on solar energy, Apache Solr provides efficiency and scalability that enables Vufind to react in milliseconds to search queries. It can be distributed if you need to spread the inventory load over many servers or in a server farm setting.
VuFind is fully modular, so you can just implement the fundamental scheme or all the parts.
And since it’s open source, you can change the modules to best suit your needs, or you can add fresh modules to extend your resource offerings.
Download Vufind
If you find this article helpful / informative then, Subscribe our site for latest education news update :
http://firsteducationnews.com
0 notes
Text
Data Persistence
Introduction to Data Persistence
Information systems process data and convert them into information.
The data should persist for later use;
To maintain the status
For logging purposes
To further process and derive knowledge
Data can be stored, read, updated/modified, and deleted.
At run time of software systems, data is stored in main memory, which is volatile.
Data should be stored in non-volatile storage for persistence.
Two main ways of storing data
- Files
- Databases
Data, Files, Databases and DBMSs
Data : Data are raw facts and can be processed and convert into meaningful information.
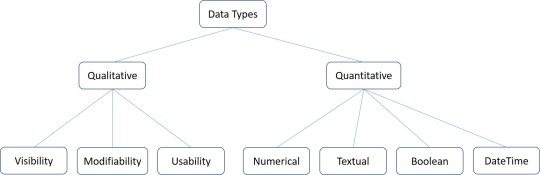
Data Arrangements
Un Structured : Often include text and multimedia content.
Ex: email messages, word processing documents, videos, photos, audio files, presentations, web pages and many other kinds of business documents.
Semi Structured : Information that does not reside in a relational database but that does have some organizational properties that make it easier to analyze.
Ex: CSV but XML and JSON, NoSQL databases
Structured : This concerns all data which can be stored in database SQL in table with rows and columns
Databases : Databases are created and managed in database servers
SQL is used to process databases
- DDL - CRUD Databases
- DML - CRUD data in databases
Database Types
Hierarchical Databases
In a hierarchical database management systems (hierarchical DBMSs) model, data is stored in a parent-children relationship nodes. In a hierarchical database model, data is organized into a tree like structure.
The data is stored in form of collection of fields where each field contains only one value. The records are linked to each other via links into a parent-children relationship. In a hierarchical database model, each child record has only one parent. A parent can have multiple children
Ex: The IBM Information Management System (IMS) and Windows Registry
Advantages : Hierarchical database can be accessed and updated rapidly
Disadvantages : This type of database structure is that each child in the tree may have only one parent, and relationships or linkages between children are not permitted
Network Databases
Network database management systems (Network DBMSs) use a network structure to create relationship between entities. Network databases are mainly used on a large digital computers.
A network database looks more like a cobweb or interconnected network of records.
Ex: Integrated Data Store (IDS), IDMS (Integrated Database Management System), Raima Database Manager, TurboIMAGE, and Univac DMS-1100
Relational Databases
In relational database management systems (RDBMS), the relationship between data is relational and data is stored in tabular form of columns and rows. Each column if a table represents an attribute and each row in a table represents a record. Each field in a table represents a data value.
Structured Query Language (SQL) is a the language used to query a RDBMS including inserting, updating, deleting, and searching records.
Ex: Oracle, SQL Server, MySQL, SQLite, and IBM DB2
Object Oriented model
Object DBMS's increase the semantics of the C++ and Java. It provides full-featured database programming capability, while containing native language compatibility.
It adds the database functionality to object programming languages.
Ex: Gemstone, ObjectStore, GBase, VBase, InterSystems Cache, Versant Object Database, ODABA, ZODB, Poet. JADE
Graph Databases
Graph Databases are NoSQL databases and use a graph structure for sematic queries. The data is stored in form of nodes, edges, and properties.
Ex: The Neo4j, Azure Cosmos DB, SAP HANA, Sparksee, Oracle Spatial and Graph, OrientDB, ArrangoDB, and MarkLogic
ER Model Databases
An ER model is typically implemented as a database.
In a simple relational database implementation, each row of a table represents one instance of an entity type, and each field in a table represents an attribute type.
Document Databases
Document databases (Document DB) are also NoSQL database that store data in form of documents.
Each document represents the data, its relationship between other data elements, and attributes of data. Document database store data in a key value form.
Ex: Hadoop/Hbase, Cassandra, Hypertable, MapR, Hortonworks, Cloudera, Amazon SimpleDB, Apache Flink, IBM Informix, Elastic, MongoDB, and Azure DocumentDB
DBMSs : DBMSs are used to connect to the DB servers and manage the DBs and data in them
Data Arrangements
Data warehouse
Big data
- Volume
- Variety
- Velocity
Applications to Files/DB
Files and DBs are external components
Software can connect to the files/DBs to perform CRUD operations on data
- File – File path, URL
- Databases – Connection string
To process data in DB
- SQL statements
- Prepared statements
- Callable statements
Useful Objects
o Connection
o Statement
o Reader
o Result set
SQL Statements - Execute standard SQL statements from the application
Prepared Statements - The query only needs to be parsed once, but can be executed multiple times with the same or different parameters.
Callable Statements - Execute stored procedures
ORM
Stands for Object Relational Mapping
Different structures for holding data at runtime;
- Application holds data in objects
- Database uses tables
Mismatches between relational and object models
o Granularity – Object model has more granularity than relational model.
o Subtypes – Subtypes are not supported by all types of relational databases.
o Identity – Relational model does not expose identity while writing equality.
o Associations – Relational models cannot determine multiple relationships while looking into an object domain model.
o Data navigations – Data navigation between objects in an object network is different in both models.
ORM implementations in JAVA
JavaBeans
JPA (JAVA Persistence API)
Beans use POJO
POJO stands for Plain Old Java Object.
It is an ordinary Java object, not bound by any special restriction
POJOs are used for increasing the readability and re-usability of a program
POJOs have gained most acceptance because they are easy to write and understand
A POJO should not;·
Extend pre-specified classes
Implement pre-specified interfaces
Contain pre-specified annotations
Beans
Beans are special type of POJOs
All JavaBeans are POJOs but not all POJOs are JavaBeans
Serializable
Fields should be private
Fields should have getters or setters or both
A no-arg constructor should be there in a bean
Fields are accessed only by constructor or getters setters
POJO/Bean to DB
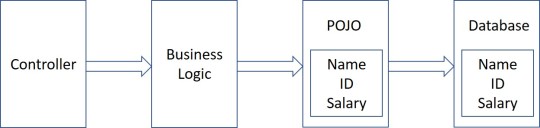
Java Persistence API
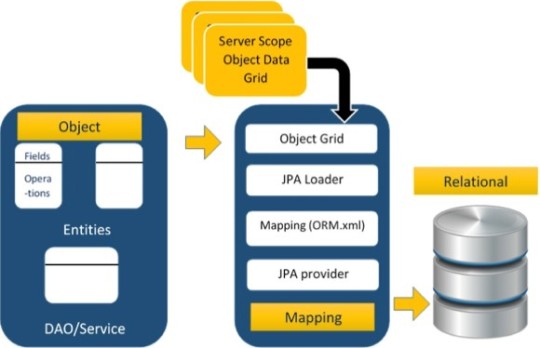
The above architecture explains how object data is stored into relational database in three phases.
Phase 1
The first phase, named as the Object data phase contains POJO classes, service interfaces and classes. It is the main business component layer, which has business logic operations and attributes.
Phase 2
The second phase named as mapping or persistence phase which contains JPA provider, mapping file (ORM.xml), JPA Loader, and Object Grid
Phase 3
The third phase is the Relational data phase. It contains the relational data which is logically connected to the business component.
JPA Implementations
Hybernate
EclipseLink
JDO
ObjectDB
Caster
Spring DAO
NoSQL and HADOOP
Relational DBs are good for structured data and for semi-structured and un-structured data, some other types of DBs can be used.
- Key value stores
- Document databases
- Wide column stores
- Graph stores
Benefits of NoSQL
Compared to relational databases, NoSQL databases are more scalable and provide superior performance
Their data model addresses several issues that the relational model is not designed to address
NoSQL DB Servers
o MongoDB
o Cassandra
o Redis
o Hbase
o Amazon DynamoDB
HADOOP
It is a framework that allows for the distributed processing of large data sets across clusters of computers using simple programming models
It is designed to scale up from single servers to thousands of machines, each offering local computation and storage
HADOOP Core Concepts
HADOOP Distributed File System
- A distributed file system that provides high-throughput access to application data
HADOOP YARN
- A framework for job scheduling and cluster resource management
HADOOP Map Reduce
- A YARN-based system for parallel processing of large data sets
Information Retrieval
Data in the storages should be fetched, converted into information, and produced for proper use
Information is retrieved via search queries
1. Keyword Search
2. Full-text search
The output can be
1. Text
2. Multimedia
The information retrieval process should be;
Fast/performance
Scalable
Efficient
Reliable/Correct
Major implementations
Elasticsearch
Solr
Mainly used in search engines and recommendation systems
Additionally may use
Natural Language Processing
AI/Machine Learning
Ranking
References
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/jpa/jpa_orm_components.htm
https://www.c-sharpcorner.com/UploadFile/65fc13/types-of-database-management-systems/
0 notes
Text
Apigee Developer
Title : Apigee Developer Location : Sunnyvale, CA Duration : 6 - 12+ Months Rate : Market Technical Skills & Knowledge: Primary Skills: APIGEE, Scala, Java Responsibilities: Build distributed, scalable, and reliable data pipelines that ingest and process?data at scale and in real-time. Collaborate with other teams to design and develop and deploy data tools that support both operations and product use cases. Perform offline analysis of large data sets using components from the Hadoop ecosystem. Evaluate and advise on technical aspects of open work requests in the product backlog with the project lead. Own product features from the development phase through to production deployment. Evaluate big data technologies and prototype solutions to improve our data processing architecture. BS in Computer Science or related area Around 6 years software development experience Minimum 2 Year Experience on Big Data Platform Must have active current experience with Scala, Java, Python, Oracle, HBase, Hive Flair for data, schema, data model, how to bring efficiency in big data related life cycle APIGEE Understanding of automated QA needs related to Big data Understanding of various Visualization platformd Experience in Cloud providers like AWS preferable Proficiency with agile or lean development practices Strong object-oriented design and analysis skills Excellent written and verbal communication skills Qualifications Top skill sets / technologies in the ideal candidate: Programming language -- Java (must), Python, Scala Database/Search ? Oracle, complex SQL queries, stored procedures, performance tuning concepts, SOLR, AWS RDS, AWS Aurora Batch processing -- Hadoop MapReduce, Cascading/Scalding, Apache Spark, AWS EMR Stream processing -- Spark streaming, Kafka, Apache Storm, Flink NoSQL -- HBase, Cassandra, MongoDB Reference : Apigee Developer jobs Source: http://jobrealtime.com/jobs/technology/apigee-developer_i3092
0 notes
Text
300+ TOP Apache SOLR Interview Questions and Answers
Apache Solr Interview Questions for freshers experienced :-
1. What is Apache Solr? Apache Solr is a standalone full-text search platform to perform searches on multiple websites and index documents using XML and HTTP. Built on a Java Library called Lucence, Solr supports a rich schema specification for a wide range and offers flexibility in dealing with different document fields. It also consists of an extensive search plugin API for developing custom search behavior. 2. What are the most common elements in solrconfig.xml? Search components Cache parameters Data directory location Request handlers 3. What file contains configuration for data directory? Solrconfig.xml file contains configuration for data directory. 4. What file contains definition of the field types and fields of documents? schema.xml file contains definition of the field types and fields of documents. 5. What are the features of Apache Solr? Allows Scalable, high performance indexing Near real-time indexing. Standards-based open interfaces like XML, JSON and HTTP. Flexible and adaptable faceting. Advanced and Accurate full-text search. Linearly scalable, auto index replication, auto failover and recovery. Allows concurrent searching and updating. Comprehensive HTML administration interfaces. Provides cross-platform solutions that are index-compatible. 6. What is Apache Lucene? Supported by Apache Software Foundation, Apache Lucene is a free, open-source, high-performance text search engine library written in Java by Doug Cutting. Lucence facilitates full-featured searching, highlighting, indexing and spellchecking of documents in various formats like MS Office docs, HTML, PDF, text docs and others. 7. What is request handler? When a user runs a search in Solr, the search query is processed by a request handler. SolrRequestHandler is a Solr Plugin, which illustrates the logic to be executed for any request.Solrconfig.xml file comprises several handlers (containing a number of instances of the same SolrRequestHandler class having different configurations). 8. What are the advantages and disadvantages of Standard Query Parser? Also known as Lucence Parser, the Solr standard query parser enables users to specify precise queries through a robust syntax. However, the parser’s syntax is vulnerable to many syntax errors unlike other error-free query parsers like DisMax parser. 9. What all information is specified in field type? A field type includes four types of information: Name of field type. Field attributes. An implementation class name. If the field type is Text Field , a description of the field analysis for the field type. 10. Explain Faceting in Solr? As the name suggests, Faceting is the arrangement and categorization of all search results based on their index terms. The process of faceting makes the searching task smoother as users can look for the exact results. 11. Define Dynamic Fields? Dynamic Fields are a useful feature if users by any chance forget to define one or more fields. They allow excellent flexibility to index fields that have not been explicitly defined in the schema. 12. What is Field Analyzer? Working with textual data in Solr, Field Analyzer reviews and checks the filed text and generates a token stream. The pre-process of analyzing of input text is performed at the time of searching or indexing and at query time. Most Solr applications use Custom Analyzers defined by users. Remember, each Analyzer has only one Tokenizer. 13. What is the use of tokenizer? It is used to split a stream of text into a series of tokens, where each token is a subsequence of characters in the text. The token produced are then passed through Token Filters that can add, remove or update the tokens. Later,that field is indexed by the resulting token stream. 14. What is phonetic filter? Phonetic filter creates tokens using one of the phonetic encoding algorithms in the org.apache.commons.codec.language package. 15. What is SolrCloud? Apache Solr facilitates fault-tolerant, high-scalable searching capabilities that enable users to set up a highly-available cluster of Solr servers. These capabilities are well revered as SolrCloud. 16. What is copying field? It is used to describe how to populate fields with data copied from another field. 17. What is Highlighting? Highlighting refers to the fragmentation of documents matching the user’s query included in the query response. These fragments are then highlighted and placed in a special section, which is used by clients and users to present the snippets. Solr consists of a number of highlighting utilities having control over different fields. The highlighting utilities can be called by Request Handlers and reused with standard query parsers. 18. Name different types of highlighters? There are 3 highlighters in Solr: Standard Highlighter : provides precise matches even for advanced queryparsers. FastVector Highlighter : Though less advanced than Standard Highlighter, it works better for more languages and supports Unicode breakiterators. Postings Highlighter : Much more precise, efficient and compact than the above vector one but inappropriate for a more number of query terms. 19. What is the use of stats.field? It is used to generate statistics over the results of arbitrary numeric functions. 20. What command is used to see how to use the bin/Solr script? Execute $ bin/Solr –helpto see how to use the bin/Solr script. 21. Which syntax is used to stop Solr? $ bin/solr stop -p 8983 is used to stop Solr. 22. Which command is used to start Solr in foreground? $ bin/solr start –f is used to start Solr in foreground. 23. What syntax is used to check whether Solr is currently running or not? $ bin/solr status is used to check Solr running status. 24. Give the syntax to start the server. $ bin/solr start is used to start the server. 25. How to shut down Apache Solr? Solr is shut down from the same terminal where it was launched. Click Ctrl+C to shut it down. 26. What data is specified by Schema? Schema declares – how to index and search each field. what kinds of fields are available. what fields are required. what field should be used as the unique/primary key 27. Name the basic Field types in Solr? date long double text float Become Master of Apache Solr by going through this online Solr Training. 28. How to install Solr? The three steps of Installation are: Server-related files, e.g. Tomcat or start.jar (Jetty). Solr webapp as a .war. Solr Home which comprises the data directory and configuration files 29. What are the important configuration files of Solr? Solr supports two important configuration files solrconfig.xml. schema.xml Apache Solr Questions and Answers Pdf Download Read the full article
0 notes
Text
December 19, 2019 at 10:00PM - The Full Stack Web Development Bundle (pay what you want) Ashraf
The Full Stack Web Development Bundle (pay what you want) Hurry Offer Only Last For HoursSometime. Don't ever forget to share this post on Your Social media to be the first to tell your firends. This is not a fake stuff its real.
Full Stack development refers to the complete creation of all facets of an app or website, from front end to back end, to databasing, debugging, and testing. In sum, being a Full Stack developer can be incredibly lucrative, although getting there can be tough considering the diverse amount of education you must receive. This course is different. Covering all aspects of the development cycle, this immersive course will teach you all the tools and techniques needed to become a Full Stack developer, allowing you greater freedom on your own projects, while greatly increasing your market value as a developer.
Access 207 lectures & 33.5 hours of content 24/7
Learn front end technologies like HTML5, CSS3, Twitter Bootstrap, JavaScript, & more
Master back end tools like Nose.js, Meteor.js, Angular 2, PHP, & Ruby on Rails
Explore databasing w/ MySQL, MongoDB, Apache Cassandra, & more
Dive into Memcahced, Redis, Apache Lucene, & Apache Solr
Debug like a pro & understand important version control technologies
Create complete, functional projects using the various tools you learn
ReactJS is a JavaScript library that has changed the way front end development is done, and has become one of the most sought after skills in the tech industry. This course covers the React APIs that make creating interactive UIs a much simpler and faster process, as well as a variety of associated technologies like JavaScript, jQuery, Twitter Bootstrap, and much more.
Access 56 lectures & 8 hours of content 24/7
Learn app development processes & techniques w/ ReactJS
Cover associated technologies like core JavaScript, Firebase, MongoDB, & more
Explore the latest API versions across a variety of technologies
Build real, functional projects using ReactJS
JavaScript may enable developers to quickly build robust, scalable apps, but the jQuery library further expedites JavaScript Web development by simplifying client-side HTML scripting. This course will acquaint you with this dynamic duo, walk you through 10 projects encompassing everything from YouTube API integration to content slider creation, and teach you the art of crafting dynamic, feature-rich apps without breaking a sweat.
Master JavaScript & jQuery by building working apps & features over 50 lectures & 9 hours
Utilize supplementary languages & technologies: HTML5, CSS3, GitHub, etc.
Craft statements using variables, loops, arrays & more
Build interactive features such as content, accordion & Apple-style image sliders
Use the YouTube Data API w/ the “search . list’ method & the FancyBox lightbox script
Create a plugin & upload it to the jQuery.com plugin registry
Use the jQuery Mobile framework to craft a mobile app
ReactJS and Flux were both created by Facebook to simplify the coding process. ReactJS is a powerful JavaScript library that helps you easily create interactive UI components and reuse them in other projects. Flux is an app architecture used for creating dynamic, client-side JavaScript web applications that manages scalability, allowing you to present apps appropriately across different platforms, from desktops to mobile devices. Over this course, you’ll learn how to use both of these technologies by building ten individual projects.
Access 60 lectures & 11 hours of content 24/7
Use Bootstrap to create basic React components
Learn how to use ReactJS to create a UI & fetch data from the Github API
Create a movie find databases that uses the OMDB API to fetch movies from the database
Build a contact list & use Firebase database tech to organize it
Design a fully-functional search engine using the DuckDuckGo API
Add YouTube videos to a video gallery using just the ID of the video
Create your own functional chat application
Build a workout logger that will teach you how to create local storage
MongoDB has quickly become one of the most popular NoSQL database solutions available, and will quickly enhance your ability to handle data with ease. With a document-based approach, MongoDB lets professionals model data however they prefer. While MySQL limits modeling to rows and columns, MongoDB is much more flexible, allowing developers to use a familiar programming language like Ruby, and a JSON format. What does this mean? Faster and more intuitive storage of data.
Utilize MongoDB to manage data more efficiently w/ 67 lectures & 12 hours of content
Develop quickly w/ a document-based approach
Utilize JavaScript to communicate w/ MongoDB for faster development
Study best practices for NoSQL development
Get querying capabilities w/ the flexibility of storing data in an intuitive manner
Get familiar with PHP by building ten real, functional projects across this course. You’ll dive into ten unique PHP frameworks to get a complete understanding of how this powerful scripting language can be used to create interactive apps. Regardless of your experience, this course will give you a multi-faceted background in web development using an especially popular programming language.
Access 87 lectures & 17.5 hours of content 24/7
Create a patient manager using the CakePHP framework
Design a job board using the Yii2 framework
Build an event calendar w/ the Symfony framework
Learn how to design a photo gallery w/ the Laravel framework
Make an idea diary using the Nette framework
Design a weblink manager w/ the PHPixie framework
Further strengthen your JavaScript skills with Node.js, an open source cross-platform environment for creating server-side and network apps. This course will walk you through 10 projects through which you’ll gain practical experience in a number of important Node.js technologies, including HTML, CSS, NoSQL, and much more. By the time you’re finished, you’ll know all you need to create Web apps that are lightweight and highly scalable.
Gain experience in Node.js by completing 10 projects across 16 hours of instruction
Learn about a number of different Web technologies: HTML, CSS, NoSQL & more
Quickly & easily create lightweight, highly scalable Web apps
Dive into both front-end & back-end development principles
Design & build user interfaces for different apps
Implement different features including password encryption, user registration, etc.
Add a valuable skill set to your development repertoire
If you’ve ever considered becoming a web developer, there is no better way to start than by diving into HTML5 and JavaScript, two of the most advanced web programming languages in use today. In this course, you’ll learn by actually using HTML5, JavaScript and other tools to build a variety of fully-functioning apps, games, and websites. By the end of this course you’ll be well on your way towards a profitable career in front-end development and have 10 projects to boost your portfolio.
Access 52 lectures & 15.5 hours of content
Learn & apply concepts to 10 real-life games, apps, and sites
Become a front-end expert developing unique apps & responsive websites
Develop the front-end for a blog using tags, forms, CSS3 & responsive design
Create an animated image gallery, a sticky note app & a snake game
Master the Drag and Drop Image Uploader
Expand your client base & update your resume to advance your career
from Active Sales – SharewareOnSale https://ift.tt/2mNTFY8 https://ift.tt/eA8V8J via Blogger https://ift.tt/2s4Aeml #blogger #bloggingtips #bloggerlife #bloggersgetsocial #ontheblog #writersofinstagram #writingprompt #instapoetry #writerscommunity #writersofig #writersblock #writerlife #writtenword #instawriters #spilledink #wordgasm #creativewriting #poetsofinstagram #blackoutpoetry #poetsofig
0 notes
Text
#Solr Query Syntax#Apache Solr Query Language#Solr Search Query Examples#Solr Query Parameters#Solr Query Filters#Solr Advanced Query Syntax#solr query#solr in query#Master Solr Query Syntax
0 notes
Text
The growth of cognitive search in the enterprise, and why it matters
Enterprises typically have countless data buckets to wrangle (upwards of 93% say they’re storing data in more than one place), and some of those buckets invariably become underused or forgotten. A Forrester survey found that between 60% and 73% of all data within corporations is never analyzed for insights or larger trends, while a separate Veritas report found that 52% of all information stored by organizations is of unknown value. The opportunity cost of this unused data is substantial — the Veritas report pegs it as a cumulative $3.3 trillion by the year 2020, if the current trend holds.
That’s perhaps why this year saw renewed interest from the corporate sector in AI-powered software-as-a-service (SaaS) products that ingest, understand, organize, and query digital content from multiple sources. “Keyword-based enterprise search engines of the past are obsolete. Cognitive search is the new generation of enterprise search that uses [AI] to return results that are more relevant to the user or embedded in an application issuing the search query,” wrote Forrester analysts Mike Gualtieri, Srividya Sridharan, and Emily Miller in a comprehensive survey of the industry published in 2017.
Emerging products
Microsoft kicked the segment into overdrive in early November by launching Project Cortex, a service that taps AI to automatically classify and analyze an organization’s documents, conversations, meetings, and videos. It’s in some ways a direct response to Google Cloud Search, which launched July 2018. Like Project Cortex, Cloud Search pulls in data from a range of third-party products and services running both on-premises and in the cloud, relying on machine learning to deliver query suggestions and surface the most relevant results. Not to be outdone, Amazon last week unveiled AWS Kendra, which taps a library of connectors to unify data sources, including file systems, websites, Box, DropBox, Salesforce, SharePoint, relational databases, and more.
Of course, Google, Amazon, and Microsoft aren’t the only cognitive search vendors on the block. There’s IBM, which offers a data indexing and query processing service dubbed Watson Explorer, and Coveo, which uses AI to learn users’ behaviors and return results that are most relevant to them. Hewlett-Packard Enterprise’s IDOL platform supports analytics for speech, images, and video, in addition to unstructured text. And both Lucidworks and Squirro leverage open source projects like Apache Solr and Elasticsearch to make sense of disparate data sets.
The cognitive search market is exploding — it’s anticipated to be worth $15.28 billion by 2023, up from $2.59 billion in 2018, according to Markets and Markets — and it coincides with an upswing in the adoption of AI and machine learning in the enterprise. But it’s perhaps more directly attributable to the wealth of telemetry afforded by modern corporate digital environments.
AI under the hood
AI models like those at the heart of AWS Kendra, Project Cortex, and Cloud Search learn from signals, or behavioral data derived from various inputs. These come from the web pages that employees visit or the videos they watch online, or their online chats with support agents and public databases of support tickets. That’s not to mention detailed information about users, including job titles, locations, departments, coworkers, and potentially all of the documents, emails, and other correspondences they author.
Each signal informs an AI system’s decision-making such that it self-improves practically continuously, automatically learning how various resources are relevant to each person and ranking those resources accordingly. Plus, because enterprises have far fewer data sources to contend with than, say, a web search engine, the models are less expensive and computationally time-consuming to train.
The other piece of the puzzle is natural language processing (NLP), which enables platforms like AWS Kendra to understand not only the document minutiae, but the search queries that employees across an organization might pose — like “How do I invest in our company’s 401k?” versus “What are the best options for my 401k plan?”
Not every platform is equally capable in this regard, but most incorporate emerging techniques in NLP, as well as the adjacent field of natural language search (NLS). NLS is a specialized application of AI and statistical reasoning that creates a “word mesh” from free-flowing text, akin to a knowledge graph, to connect similar concepts that are related to larger ideas. NLS systems understand context in this way, meaning they’ll return the same answer regardless of how a query is phrased and will take users to the exact spot in a record where that answer is likely to be found.
Cognitive search: the new normal
In short order, cognitive search stands to become table stakes in the enterprise. It’s estimated that 54% of knowledge workers are already interrupted a few times or more per month when trying to get access to answers, insights, and information. And the volume of unstructured data organizations produce is projected to increase in the years to come, exacerbating the findability problem.
“Productivity isn’t just about being more efficient. It’s also about aggregating and applying the collective knowledge of your organization so that together you can achieve more,” wrote Microsoft 365 corporate vice president Jared Spataro in a recent blog post. “[Cognitive search systems enable] business process efficiency by turning your content into an interactive knowledge repository … to analyze documents and extract metadata to create sophisticated content models … [and to] make it easy for people to access the valuable knowledge that’s so often locked away in documents, conversations, meetings, and videos.”
The post The growth of cognitive search in the enterprise, and why it matters appeared first on Actu Trends.
0 notes
Text
What is solr developer task & its importance?
Apache Solr is a popular enterprise-level search platform which is being used widely by popular websites such as Reddit, Netflix, and Instagram. The reason for the popularity of Apache Solr is its well-built text search, faceted search, real-time indexing, dynamic clustering, and easy integration. Apache Solr helps building high level search options for the websites containing high volume data. Enhance your Business with Solr If you have a website with a large number of documents, you must need good content management architecture to manage search functionality. Let it be an e-commerce portal with numerous products or website with thousand pages of lengthy content, it is hard to search for what you exactly want. Here comes integrated Solr with a content management system to help you with fast and effective document search. At Prominent Pixel, we offer comprehensive consulting services for Apache Solr for eCommerce websites, content-based websites, and internal enterprise-level content management systems.
What we do Our Solr Solution & Services Leading search solution provider for Terabyte sized, Customized, Scalable search solutions. Consulting for Solr Architectural Design Our Solr consulting services include Search application assessment, Solr strategy consulting, Solr search engine tuning, Migration, Managed services, Support and Training, and Big Data application consulting and implementation.
Custom CMS Integration Things are made easy with one click CMS integration with Solr. Hire dedicated Apache Solr developer from Prominent Pixel for the best custom CMS integration. Our developers are experts in Drupal and Solr integration which helps your business grow.
Solr Installation & Configuration Our dedicated Apache Solr developers will install Solr on the right platform by choosing the Java Runtime Environment with the right version. After the installation process, our developers will configure on module level. Disaster Recovery and Replication Hire our Apache Solr developers to get help in indexing corruption issues, malicious administrative actions, accidental data entry or subtractions. Also, we ensure redundancy for your data through replication.
Solr Plugin Development The Solr framework helps easy plugin development that extends the capability of the software to the maximum. Hire dedicated Apache Solr developers from Prominent Pixel to get custom Solr plugins.
Solr Performance Tuning, Load Balancing and Load Testing Our dedicated Apache Solr developers will help you maximize the Solr performance by conducting performance tuning, load balancing, and load testing. Choose and hire our Solr developer right now to accomplish your goals. What we do Our Technical Skills & Key Strengths Our core expertise is in Solr Architectural Design, Custom plugin development for Solr & Solr custom Solutions. Development Skills Our Solr Developers have years of experience and expertise in developing Solr plugins and websites. Hire our dedicated Apache Solr development programmers to get your work done perfectly. Tools Our Apache Solr developers use core-specific tools as well as collection-specific tools depending on the requirement of your project. Concept Comprehensive administrative interface, easy monitoring, Near real-time indexing, Extensible plugin architecture, High volume traffic, and more. Why Hire Solr Developers From Prominent Pixel? Prominent Pixel has a team of expert and experienced Apache Solr developers who have worked on several Solr projects to date. Our developers’ will power up your enterprise search with flexible features of Solr. Our Solr services are specially designed for eCommerce websites, content-based websites and enterprise-level websites. Also, our dedicated Apache Solr developers create new websites with solar integrated content architecture. Why us? Key Benefits Apache Solr is preferred for its powerful search technology which has rich features that reduces the overall search time. The easy integration with Content Management Systems like Drupal, Wordpress, and e-commerce platforms like Magento, OpenCart, WooCommerce, and others is the reason why you should choose Apache Solr development. Powerful Extensions Solr comes with optional plugins with indexing rich content, language detection, search results clustering, and much more. Advanced Configurable Search Analysis Solr supports many languages, such as English, Chinese, Japanese, German, French etc. Also, there are many analysis tools for indexing and querying the content flexibly. Built-in Security You can secure Solr with SSL, Authentication, and Role-based authorization. Full-Text Search The advanced full-search options of Apache Solr include excellent matching abilities such as wildcards, phrases, joins, grouping and much more. Open Interfaces with Rich Standards Building an app has become much easier with Solr by using open interfaces like XML, HTTP, and more. Solr Optimization Optimized for high volume traffic and proved to the world at a large scale. Our dedicated Solr developer helps you optimize for high traffic that you have ever expected. Our Hiring Process We offer personalized and flexible pricing packages to our clients. Hire full time, part time or hourly basis as per your needs.
0 notes
Text
Original Post from Trend Micro Author: Trend Micro
By: Santosh Subramanya (Vulnerability Researcher)
Security researcher Michael Stepankin reported a vulnerability found in the popular, open-source enterprise search platform Apache Solr: CVE-2019-0192. It’s a critical vulnerability related to deserialization of untrusted data. To have a better understanding of how the vulnerability works, we replicated how it could be exploited in a potential attack by using a publicly available proof of concept (PoC).
Successfully exploiting this security flaw can let hackers execute arbitrary code in the context of the server application. For example, an unauthenticated hacker can exploit CVE-2019-0192 by sending a specially crafted Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) request to the Config API, which allows Apache Solr’s users to set up various elements of Apache Solr (via solrconfig.xml). Affected versions include Apache Solr 5.0.0 to 5.5.5 and 6.0.0 to 6.6.5.
What is Apache Solr? Apache Solr is an open-source enterprise search platform built on Apache Lucene, a Java-based library. It reportedly has a 35-percent market share among enterprise search platforms and is used by various multinational organizations.
Designed to be scalable, Apache Solr can index, query, and map sites, documents, and data from a variety of sources, and then return recommendations for related content. It supports text search, hit highlighting, database integration, and document handling (e.g., Word and PDF files) among others. It also supports JavaScript object notation (JSON) representational state transfer (REST) application programming interfaces (APIs). This means Apache Solr can be integrated with compatible systems or programming languages that support them. Apache Solr runs on port 8983.
What is CVE-2019-0192? The vulnerability is caused by an insufficient validation of request to the Config API, which lets Apache Solr’s users configure solrconfig.xml. This solrconfig.xml, in turn, controls how Apache Solr behaves in the installed system by mapping requests to different handlers. Parameters in solrconfig.xml, for instance, define how search requests and data are processed, managed, or retrieved.
Apache Solr is built on Java, which allows objects to be serialized, that is, converting and representing objects into a compact byte stream. This makes it a convenient way for the objects to be transferred over network. It can then be deserialized for use by a Java virtual machine (JVM) receiving the byte stream.
Config API allows Solr’s Java management extensions (JMX) server to be configured via HTTP POST request. An attacker could point the JMX server to a malicious remote method invocation (RMI) server and take advantage of the vulnerability to trigger remote code execution (RCE) on the Solr server.
How does CVE-2019-0192 work? An attacker can start a malicious RMI server by running a command, as seen in our example in Figure 1 (top). The ysoserial payload with class JRMPListener can be used to embed the command touch /tmp/pwn.txt, which can then get executed on a vulnerable Apache Solr. A POST request (Figure 1, bottom) can then be sent to Solr to remotely set the JMX server.
Figure 1. Snapshots of code showing how a malicious RMI server is started (top), and how a POST request is sent (bottom)
JMX enables remote clients to connect to a JVM and monitor the applications running in that JVM. The applications can be managed via managed beans (MBeans), which represents a resource. Through MBeans, developers, programmers, and Apache Solr users can access and control the inner workings of the running application. MBeans can be accessed over a different protocol via Java RMI. Apache Solr users who want to use JMX/RMI interface on a server can accordingly create a JMXService URL (service:jmx:rmi:///jndi/rmi://:/jmxrmi).
In the example showed in Figure 2, the attacker, exploiting CVE-2019-0192, could use a POST request and set the JMXService URL (jmx.serviceUrl) remotely via Config API using the ‘set-property’ JSON object.
As shown in Figure 3, it would return a 500 error, including the string “undeclared checked exception; nested exception is” in the response body.
Figure 2. Code snapshot showing how the JMXService could be set remotely
Figure 3. Snapshot of code showing the error 500
Due to improper validation, this jmx.serviceUrl can be pointed to an attacker-controlled JMRP listener (which is typically used to notify about events or conditions that occur). This causes the vulnerable Apache Solr to initiate an RMI connection to a malicious JMRP Listener. A three-way handshake will then be initiated with the malicious RMI server to set up a connection with the malicious RMI server.
An attacker can then take advantage of this to carry out RCE on the vulnerable Apache Solr. As shown in Figure 4, an attacker, for instance, can send a maliciously crafted serialized object.
Figure 4. Snapshot showing data transmission after exploiting CVE-2019-0192
How to address this vulnerability Apache Solr recommends patching or upgrading to 7.0 (or later) versions. It’s also advised to disable or restrict Config API when not in use. The network should also be proactively configured and monitored for any anomalous traffic that may be running on hosts that has Apache Solr installed.
Developers, programmers, and system administrators using and managing Apache Solr should also practice security by design as well as enforce the principle of least privilege and defense in depth to protect against threats that may exploit this vulnerability.
The Trend Micro Deep Security and Vulnerability Protection solutions protect user systems from threats that may exploit CVE-2019-0192 via this Deep Packet Inspection (DPI) rule:
1009601 – Apache Solr Remote Code Execution Vulnerability (CVE-2019-0192)
Trend Micro TippingPoint customers are protected from attacks that exploit CVE-2019-0192 this MainlineDV filter:
313798 – HTTP: Apache Solr Java Unserialized Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
The post CVE-2019-0192: Mitigating Unsecure Deserialization in Apache Solr appeared first on .
#gallery-0-5 { margin: auto; } #gallery-0-5 .gallery-item { float: left; margin-top: 10px; text-align: center; width: 33%; } #gallery-0-5 img { border: 2px solid #cfcfcf; } #gallery-0-5 .gallery-caption { margin-left: 0; } /* see gallery_shortcode() in wp-includes/media.php */
Go to Source Author: Trend Micro CVE-2019-0192: Mitigating Unsecure Deserialization in Apache Solr Original Post from Trend Micro Author: Trend Micro By: Santosh Subramanya (Vulnerability Researcher) Security researcher Michael Stepankin…
0 notes
Text
Apigee Developer
Title : Apigee Developer Location : Sunnyvale, CA Duration : 6 - 12+ Months Rate : Market Technical Skills & Knowledge: Primary Skills: APIGEE, Scala, Java Responsibilities: Build distributed, scalable, and reliable data pipelines that ingest and process?data at scale and in real-time. Collaborate with other teams to design and develop and deploy data tools that support both operations and product use cases. Perform offline analysis of large data sets using components from the Hadoop ecosystem. Evaluate and advise on technical aspects of open work requests in the product backlog with the project lead. Own product features from the development phase through to production deployment. Evaluate big data technologies and prototype solutions to improve our data processing architecture. BS in Computer Science or related area Around 6 years software development experience Minimum 2 Year Experience on Big Data Platform Must have active current experience with Scala, Java, Python, Oracle, HBase, Hive Flair for data, schema, data model, how to bring efficiency in big data related life cycle APIGEE Understanding of automated QA needs related to Big data Understanding of various Visualization platformd Experience in Cloud providers like AWS preferable Proficiency with agile or lean development practices Strong object-oriented design and analysis skills Excellent written and verbal communication skills Qualifications Top skill sets / technologies in the ideal candidate: Programming language -- Java (must), Python, Scala Database/Search ? Oracle, complex SQL queries, stored procedures, performance tuning concepts, SOLR, AWS RDS, AWS Aurora Batch processing -- Hadoop MapReduce, Cascading/Scalding, Apache Spark, AWS EMR Stream processing -- Spark streaming, Kafka, Apache Storm, Flink NoSQL -- HBase, Cassandra, MongoDB Reference : Apigee Developer jobs source http://www.qoholic.com/jobs/technology/apigee-developer_i4551
0 notes
Text
Apigee Developer
Title : Apigee Developer Location : Sunnyvale, CA Duration : 6 - 12+ Months Rate : Market Technical Skills & Knowledge: Primary Skills: APIGEE, Scala, Java Responsibilities: Build distributed, scalable, and reliable data pipelines that ingest and process?data at scale and in real-time. Collaborate with other teams to design and develop and deploy data tools that support both operations and product use cases. Perform offline analysis of large data sets using components from the Hadoop ecosystem. Evaluate and advise on technical aspects of open work requests in the product backlog with the project lead. Own product features from the development phase through to production deployment. Evaluate big data technologies and prototype solutions to improve our data processing architecture. BS in Computer Science or related area Around 6 years software development experience Minimum 2 Year Experience on Big Data Platform Must have active current experience with Scala, Java, Python, Oracle, HBase, Hive Flair for data, schema, data model, how to bring efficiency in big data related life cycle APIGEE Understanding of automated QA needs related to Big data Understanding of various Visualization platformd Experience in Cloud providers like AWS preferable Proficiency with agile or lean development practices Strong object-oriented design and analysis skills Excellent written and verbal communication skills Qualifications Top skill sets / technologies in the ideal candidate: Programming language -- Java (must), Python, Scala Database/Search ? Oracle, complex SQL queries, stored procedures, performance tuning concepts, SOLR, AWS RDS, AWS Aurora Batch processing -- Hadoop MapReduce, Cascading/Scalding, Apache Spark, AWS EMR Stream processing -- Spark streaming, Kafka, Apache Storm, Flink NoSQL -- HBase, Cassandra, MongoDB Reference : Apigee Developer jobs source http://www.qoholic.com/jobs/technology/apigee-developer_i4551
0 notes
Text
Apigee Developer
Title : Apigee Developer Location : Sunnyvale, CA Duration : 6 - 12+ Months Rate : Market Technical Skills & Knowledge: Primary Skills: APIGEE, Scala, Java Responsibilities: Build distributed, scalable, and reliable data pipelines that ingest and process?data at scale and in real-time. Collaborate with other teams to design and develop and deploy data tools that support both operations and product use cases. Perform offline analysis of large data sets using components from the Hadoop ecosystem. Evaluate and advise on technical aspects of open work requests in the product backlog with the project lead. Own product features from the development phase through to production deployment. Evaluate big data technologies and prototype solutions to improve our data processing architecture. BS in Computer Science or related area Around 6 years software development experience Minimum 2 Year Experience on Big Data Platform Must have active current experience with Scala, Java, Python, Oracle, HBase, Hive Flair for data, schema, data model, how to bring efficiency in big data related life cycle APIGEE Understanding of automated QA needs related to Big data Understanding of various Visualization platformd Experience in Cloud providers like AWS preferable Proficiency with agile or lean development practices Strong object-oriented design and analysis skills Excellent written and verbal communication skills Qualifications Top skill sets / technologies in the ideal candidate: Programming language -- Java (must), Python, Scala Database/Search ? Oracle, complex SQL queries, stored procedures, performance tuning concepts, SOLR, AWS RDS, AWS Aurora Batch processing -- Hadoop MapReduce, Cascading/Scalding, Apache Spark, AWS EMR Stream processing -- Spark streaming, Kafka, Apache Storm, Flink NoSQL -- HBase, Cassandra, MongoDB Reference : Apigee Developer jobs source http://linkhello.com/jobs/technology/apigee-developer_i3256
0 notes
Text
Apigee Developer
Title : Apigee Developer Location : Sunnyvale, CA Duration : 6 - 12+ Months Rate : Market Technical Skills & Knowledge: Primary Skills: APIGEE, Scala, Java Responsibilities: Build distributed, scalable, and reliable data pipelines that ingest and process?data at scale and in real-time. Collaborate with other teams to design and develop and deploy data tools that support both operations and product use cases. Perform offline analysis of large data sets using components from the Hadoop ecosystem. Evaluate and advise on technical aspects of open work requests in the product backlog with the project lead. Own product features from the development phase through to production deployment. Evaluate big data technologies and prototype solutions to improve our data processing architecture. BS in Computer Science or related area Around 6 years software development experience Minimum 2 Year Experience on Big Data Platform Must have active current experience with Scala, Java, Python, Oracle, HBase, Hive Flair for data, schema, data model, how to bring efficiency in big data related life cycle APIGEE Understanding of automated QA needs related to Big data Understanding of various Visualization platformd Experience in Cloud providers like AWS preferable Proficiency with agile or lean development practices Strong object-oriented design and analysis skills Excellent written and verbal communication skills Qualifications Top skill sets / technologies in the ideal candidate: Programming language -- Java (must), Python, Scala Database/Search ? Oracle, complex SQL queries, stored procedures, performance tuning concepts, SOLR, AWS RDS, AWS Aurora Batch processing -- Hadoop MapReduce, Cascading/Scalding, Apache Spark, AWS EMR Stream processing -- Spark streaming, Kafka, Apache Storm, Flink NoSQL -- HBase, Cassandra, MongoDB Reference : Apigee Developer jobs source http://cvwing.com/jobs/technology/apigee-developer_i3259
0 notes